

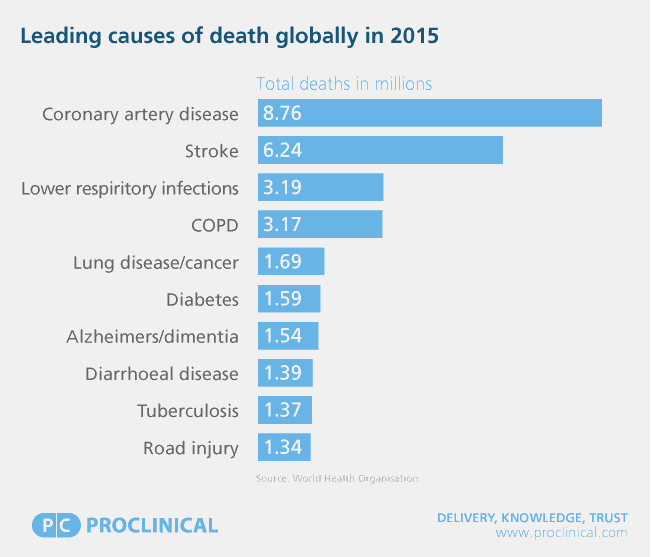
Following a survey carried out by the World Health Organisation (WHO), Proclinical has compiled a list of the top leading causes of death in the world. While some diseases are well known for causing high death rates worldwide, there are a few that may come as a surprise. It’s not all doom and gloom though, as the life sciences is always striving to make medical advances to find cures for these deadly diseases. Find out more:
10. Road accidents
Tragically, as many as 1.3 million deaths are a result of road accidents every year. It is the leading cause of accidental death. Road accidents often lead to death as the impact of a collision can cause severe injuries such as head trauma (brain swelling, haemorrhages and blood clots), external and/or internal bleeding, or a broken neck. It’s the leading cause of death among those aged 15-30, with 90% of cases occurring in developing countries, and a further 20-50 million people a year suffer vehicular-related injuries, including disability.
In the last 30 years, survival rates for road accidents have doubled. This is partly thanks to safer vehicles but also due to improvements in medical devices for diagnostics, treating wounds and replacing failed organs. With the introduction of 3D printed organs and robotic surgery, fatalities can be expected to decline further. Also, improved blood transfusion equipment has been shown decrease the time it takes to do a blood transfusion, which could mean the difference between life and death in an emergency situation.
9. Tuberculosis (TB)
TB was one of the most prevalent global epidemics in the 18th and 19th centuries. Since a cure for TB was discovered by Selman Waksman in 1943, the number of TB-related deaths declined significantly in the years following. The widespread distribution of the TB vaccine (BCG) helped to reduce cases further, although it has not been entirely effective in preventing the disease. In fact, TB remains a significant threat as one of the top 10 killers in the world. One-third of the world’s population is infected with TB bacteria every year, causing over 9 million cases and resulting in around 1.4 million deaths.
Pharmaceutical giant Sanofi is teaming up with the TB Alliance to develop new treatments for TB, including drug-resistant forms, which are becoming an increasing threat to patients. Other companies researching new treatments for TB are Otsuka Pharmaceutical and Sequella who are trialling drugs carbostyril compound OPC-167832 and SQ109, respectively.
8. Diarrhoeal diseases
Diarrhoeal diseases, including cholera and dysentery, are another leading cause of mortality, particularly in developing countries. It is the second leading cause of death in children under 5 years, killing approximately 525,000 children every year. Prolonged bouts of diarrhoea strip the person of water and vital electrolytes such as sodium and chloride, leading to fatal levels of dehydration and malnutrition. These diseases are predominantly caused by drinking unclean water and/or living in unsanitary conditions but can be easily treated with medication. However, insufficient availability of these life-saving drugs in many developing countries makes it difficult to control the widespread outbreaks, leading to 1.39 million deaths a year.
7. Alzheimer’s disease
The number of people dying from Alzheimer’s disease, the leading cause of dementia, is rapidly increasing every year (1.54 million). Alzheimer’s in a neurodegenerative disease in which patients experience a gradual decrease in cognitive ability, such as memory and speech, caused by a build-up of amyloid proteins. Currently, there is no known way to prevent or cure Alzheimer’s disease.
A lot of research is currently being undertaken by several top 10 pharmaceutical companies to understand what the causes are and if there is a possible cure for Alzheimer’s. For example, Biogen has three late-stage drugs, BAN2401 (phase II), E2609 (phase III) and Aducanumab (phase III), in its pipeline. These drugs have been effective in improving cognitive function by blocking or removing the harmful proteins. Also, Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Zinfandel Pharmaceuticals have partnered to validate a biomarker called TOMM40 to use as a test for Alzheimer’s that will help with early detection of the disease. To find out more, see our blog about the current research efforts into Alzheimer’s.
6. Diabetes
There is a growing global epidemic of diabetes that affects over 400 million people, resulting in approximately 1.59 million deaths each year. There are two types of the disease; one is an autoimmune condition whilst the other is linked to poor lifestyle choices such as diet. In both cases, the body has difficulty dealing with insulin, an agent that helps the body to absorb and process glucose. To find out some more facts about diabetes, check out our blog.
As the number of diabetes-related deaths increases, pharmaceutical companies are working to develop better treatments to help patients to manage the disease. For example, Novo Nordisk A/S is currently attempting to create a way for patients with type 1 diabetes to take their drugs via pill instead of injection, in response to growing demand. The company is in the advanced stages of testing an oral version of a GLP-1 (drugs that stimulate the pancreas) as well as oral insulin.
- 10 facts you should know about diabetes
- What does the future look like for people living with Parkinson's disease?
- What are the different phases of clinical trials?
- Is there a cure for HIV/AIDS?
5. Lung cancer, trachea and bronchus
Lung disease, particularly lung cancer, is number 5 of the top 10 killers. It is responsible for over 1.6 million deaths worldwide. Lung cancer is a particularly aggressive and serious form of cancer that is very common in smokers, accounting for 85% of cases. Countries such as Spain and Hungary are highly affected by the disease, and in China, it is the most common type of cancer.
Leading the research into lung cancer are prominent pharmaceutical companies such as AstraZeneca, Merck and Roche. In early 2017, AstraZeneca had their drug Tagrisso approved after demonstrating that it reduces many lung cancer symptoms including appetite loss, fatigue, breathlessness and chest pain. In October 2016, the FDA approved KEYTRUDA, an immunotherapy treatment developed by Merck. Immunotherapy, which involves stimulating the body’s natural immune capabilities to fight cancer, is currently a focus for many pharmaceutical companies as it has proved quite effective in treating various types of the disease. However, a lot of research is still needed to find out the full capabilities of this kind of treatment.
4. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
The fourth leading cause of death globally is a cluster of airway conditions that fall under the term chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. These include chronic bronchitis and emphysema, which are conditions that make the lungs inflamed and damaged. The main cause is smoking, although COPD can affect non-smokers, particularly asthma patients and those who live in very polluted areas. Asian populations are most affected because of high levels of pollution in countries such as Nepal, North Korea and India. COPD is estimated to be the cause of 3.17 million deaths every year.
Front-runners in research include AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK). AstraZeneca has several early and late stage COPD drugs in their pipeline, including benralizumab which has been effective so far in improving lung function. GSK also has several COPD drugs in various stages, including many in phase II and III such as mepolizumab, which has been seen as a breakthrough for patients suffering with severe asthma.
3. Lower respiratory infections
Lower respiratory infections are the deadliest communicable diseases in the world, which are triggered by viruses and bacteria. These diseases affect the patient’s lungs and airways. Examples include influenza (the flu), bronchitis and pneumonia. Global flu epidemics and pneumonia are known to cause devastation in elderly and infant populations every year. In 2015, pneumonia killed 920,136 children under the age of 5, mostly in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. The introduction of vaccines has been incredibly effective in lowering mortality rates over the past 20-30 years, particularly in developing countries.
Polypher, a Swiss pharmaceutical company, is currently trialling the drug Murepavadin, which has proved successful in treating 9 out of 10 patients with antibiotic resistant pneumonia. As the flu virus is constantly changing, the flu vaccine composition is adapted each year to make it as effective as possible.
2. Stroke
The second leading cause of death worldwide is stroke. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, causing brain cells to die. This can lead to brain injury, disability and in some cases, death. The main causes of a stroke are from a blockage/blood clot (ischaemic) or a ruptured blood vessel (haemorrhagic). Most prevalent in developing countries in South East Asia and the Caribbean, strokes account for 6.24 million deaths per year.
There has been a recent breakthrough in clinical research with PCSK9 inhibitors, which are injectable drugs that dramatically lower cholesterol levels when combined with a statin. This has been seen to lower the risk of stroke and heart attacks in patients. The first PCSK9 drugs to be approved were Sanofi and Regeneron’s alirocumab and Amgen’s evolocumab in the summer of 2015.
In early 2017 it was announced that a promising treatment for strokes is being made more widely available to patients: the mechanical thrombectomy. This is a device that can remove a stroke-causing clot with the help of clot-busting drugs, and has shown to significantly improve quality of life in the months following the stroke.
1. Ischaemic heart disease (coronary artery disease)
Topping the list of the world’s most deadly diseases is Ischaemic heart disease, more commonly known as coronary artery disease. Responsible for nearly 9 million deaths every year, heart disease is caused by a build-up of fatty deposits on the wall of the arteries, usually attributed to lifestyle choices or other conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes. This disease is deadly as the patient’s arteries become narrowed, restricting blood and oxygen flow to the heart, potentially leading to a fatal heart attack. Non-deadly attacks cause chest pain known as angina, which can proceed a heart attack. Eastern European countries such as Ukraine, Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan suffer the highest number of casualties, most likely due to the heavy drinking culture and high levels of pollution.
As the number one cause of death, it’s a major point of focus for several pharmaceutical companies, many of which are currently developing better treatments to help patients with heart disease. A global leader in cardiovascular disease is Pfizer, which has drug PF-06282999 in early clinical phase development and is continuously seeking ways to treat the causes behind cardiovascular disease. Similarly, AstraZeneca boasts a strong cardiovascular pipeline with promising drugs across all clinical phases.
If you would like to be a part of developing life-saving drugs and treatments for some of the leading global causes of mortality, consider a career in clinical research. At Proclinical Staffing, we are dedicated to helping professionals to find their ideal position working for many of these top pharmaceutical employers. Upload your CV to the Proclinical website or have a look at our current clinical research jobs, and our specialist recruitment consultants will be in touch with any suitable roles, many of which are with the top 10 pharmaceutical companies in the world.




.png)

.png)

.png)





.png)

.png)
.png)

.png)










